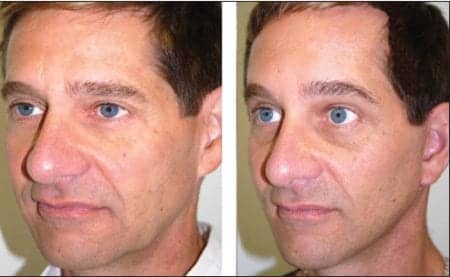
Nutricosmetic products can help support cosmetic enhancement procedures, as well as the wound-healing process.
Skin aging is a complex and natural phenomenon that is characterized by a progressive deterioration of its physical and functional properties. It is generally agreed that this phenomenon begins at age 30.
Aging of the skin is considered a degenerative process that is affected by both intrinsic and extrinsic factors. Intrinsic factors are those that occur physiologically and are related to the changes that take place on a cellular level, such as a reduction in dermoepidermal papillae in the stratum corneum, decreased thickness of the dermis, an increase in skin laxity, and a reduction in both dermal collagen as well as connective tissue components.
A number of extrinsic factors are also thought to contribute to aging of the skin, including actinic damage, smoking, and other exogenous stimuli. A number of theories seek to determine the primary causes of aging overall. While aging is the result of multifactorial events, the occurrence of inflammation, free radical damage, and oxidative stress all seem to play a role in the predominant ones. Some of these scientific proposals also surmise that the same factors that influence aging may also contribute to aging’s effects on the skin.
As the Baby Boomer generation becomes more concerned with managing the signs of aging, the cosmeceutical and nutricosmetic markets are responding to this need. These markets are becoming an important area of growth to watch. Moreover, it is interesting to note that younger demographics, aged 20 and younger, are also interested in aging—notably, from a preventive perspective.
With cutting-edge technologies, research and development, and sophisticated formulations in topical and ingestible products, a cohesive paradigm shift is taking place within traditional medical aesthetic programs. Additionally, emerging trends in cosmetic plastic surgery are not only having an effect on consumers’ desire for a youthful appearance, but are also serving as an impetus for product companies to attempt to deliver “surgical results in a pill or a bottle.”
Formulators realize that biological challenges generally originate and are solved at the cellular level, meaning that both topical and ingestible products must address the body’s cellular mechanisms to effectively protect and support the biochemical mechanisms that accelerate aging. Moreover, physicians are noting the sophisticated consumer’s demand for effective and nonirritating, naturally based products that will deliver results without toxicity. Combining cosmeceuticals and nutricosmetics along with aesthetic medical procedures is proving effective in supporting outcomes and minimizing recovery time, helping to ensure patient satisfaction.
COSMECEUTICALS: A TOPICAL APPROACH IN SKIN REJUVENATION
Demand for cosmeceutical products is expected to increase 7.2% per year, to $9.4 billion in 2012. With an increased public awareness of the potential for toxicity in more traditional, chemical-based products, these numbers demonstrate this new demand for products (or by-products) that will not disrupt the body’s constitution or physiologic function.
Cosmeceuticals are topical products containing biologically active ingredients that will have a measurable effect upon the user. This category of products arose from the combination of a cosmetic and pharmaceutical product. Although they are not officially recognized by the FDA, cosmeceuticals offer the aesthetic medical community therapeutic formulations to help change the appearance of the skin, hair, or nails.
In the past, skin care products focused heavily on the use of skin-resurfacing agents. Currently, cosmeceutical products are targeting the potential of antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and nourishing ingredients to not only improve the skin’s appearance but also to help protect the skin from environmental stressors and support dermal healing in noninvasive and invasive cosmetic procedures. These products are providing a variety of topical delivery systems that allow active ingredients such as phytosterols (also known as plant sterols), amino acids, antioxidants, ascorbic acid, and alpha hydroxy acid to penetrate the skin for effective results.

The careful, planned use of nutrition and supplements can assist in improved patient recovery time.
NUTRICOSMETICS: TARGETING AT THE CELLULAR LEVEL TO PROTECT, REPAIR, AND REJUVENATE
A more recent introduction to North America is the use of nutricosmetics. This category of products is a blend of cosmeceuticals and nutraceuticals, providing ingestible nutritional formulations aimed at improving one’s skin health and beauty, or supporting the wound-healing process.
As a category, nutricosmetics is already considered mainstream in Asian and European markets, and is an essential part of the antiaging armamentarium in these countries. Very recently, the North American consumer is beginning to more readily accept the potential efficacy of such products. According to leading market analysts, the general trend shows that the American consumer is becoming more adventurous with tastes and textures, and is becoming increasingly open to trying out new products that claim to promote beauty—particularly those products considered at least partially “natural” and that help to promote beauty from the inside out.
A nutricosmetic product contains active ingredients that can bypass several barriers, including bio-availability and bio-distribution, in order to effectively deliver its payload to the skin—the target organ. These active ingredients enter from the inside and move toward the outer layer. They are found in the deeper layers of the skin, where they can do their work effectively through protecting the skin from oxidative stress and promoting healthy skin cell turnover.
CONCERNING AESTHETIC MEDICINE PROCEDURES
While sound nutrition and a healthy lifestyle support healthy aging, nutraceuticals may further support cellular function to create the most favorable conditions. Aesthetic medicine treatments and procedures involve many different intervention tools that aim to rejuvenate skin health and beauty. However, they can involve some level of manipulation that will increase oxidative stress and offset the radical/antioxidant balance in the body.
Within aesthetic medicine, the goal of nutricosmetics is to better prepare for the procedure, accelerate healing, and help achieve enhanced and longer-lasting results. Products purported for surgical and medical aesthetic treatments may include ingredients in the form of antioxidants, amino acids, pre- and probiotics, enzymes, vitamins, and minerals.
The administration of these formulations has been shown in human clinical studies to be beneficial in reducing oxidative stress and potential complications associated with medical aesthetic procedures.
In regard to surgical procedures, nutraceuticals may support the healing process by balancing anabolic/catabolic states and minimizing postoperative oxidative stress for an improved rate of recovery. In addition, oral supplements may help to prepare the preoperative patient by supplying needed vitamins and minerals that will assist in the healing process that otherwise may have been lacking or depleted in the standard diet. Efficacious formulations containing micronutrients, antioxidants, amino acids, enzymes, and pro/prebiotics may work collectively to best support healthy immune response and minimize postoperative complications so the patient can return more quickly to their normal quality of life.
Although no product may guarantee improved healing if the patient is not healthy from the start, it is plausible to believe that nutraceuticals may serve as a beneficial complement in the preparation of the healthy patient; vis-à-vis, optimizing outcomes and reducing potential complications from excessive postoperative inflammation or delayed healing.
Some nutraceuticals also claim to address postprocedure adverse effects, such as bruising and swelling. Thus, in the candidate who is appropriate for surgery, it is reasonable to suggest that a holistic plan that incorporates nutraceuticals may help to bring about an improved overall recovery experience.
Paula Simpson, BASc (Nutrition), RNCP, is the formulator and co-founder of GliSODin Skin Nutrientsand a nutritionist, as well as a contributing editor to aesthetic and beauty publications. She can be reached via www.glisodinskin.com.
Shirley Madhère, MD, is a plastic surgeon in private practice in New York City. She can be reached via www.thenewaesthete.com or www.drshirleymadhère.com.